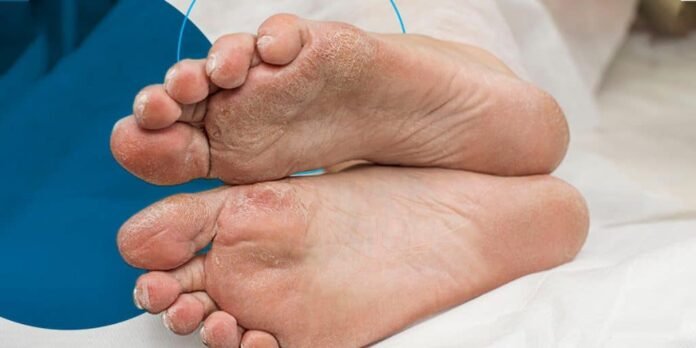
Diabetes often brings along a host of complications, with foot ulcers being one of the most prevalent and concerning issues among diabetic individuals. These ulcers can lead to severe infections and even amputations if not managed properly. Here’s a simple guide for diabetics to prevent and manage foot ulcers with five practical tips:
- Regular Foot Inspections: Diabetics should inspect their feet daily for any signs of redness, swelling, blisters, or cuts. Any wounds should be reported to a healthcare professional immediately, as even minor injuries can escalate into serious ulcers.
- Proper Foot Hygiene: Keeping the feet clean and dry is essential for preventing infections. Diabetics should wash their feet with lukewarm water and mild soap, ensuring to dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes, as moisture can promote bacterial growth.
- Wear Proper Footwear: Diabetics should opt for shoes that fit well and provide adequate support and protection. Avoiding high heels and shoes with pointed toes is crucial to prevent pressure points and rubbing that can lead to ulcers. Additionally, wearing clean, dry socks made from breathable materials is recommended.
- Maintain Healthy Blood Sugar Levels: Elevated blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to heal, increasing the risk of foot ulcers. Diabetics should monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations for medication, diet, and lifestyle modifications to keep their blood sugar within target range.
- Regular Foot Care by Healthcare Professionals: Diabetics should schedule regular foot exams with their healthcare provider or a podiatrist to monitor for any signs of ulcers or other foot problems. These professionals can also provide guidance on proper foot care techniques and recommend treatments or interventions as needed.
- Manage Peripheral Neuropathy: Diabetics often experience peripheral neuropathy, a condition characterized by nerve damage in the feet and legs. This can lead to decreased sensation, making it difficult to detect injuries or abnormalities. To manage peripheral neuropathy, individuals should inspect their feet visually if they are unable to feel them properly. Additionally, medications and treatments prescribed by healthcare professionals can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further nerve damage.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol Consumption: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can impair circulation and increase the risk of foot ulcers in diabetics. Therefore, individuals with diabetes should quit smoking and limit their alcohol intake to reduce these risks and promote overall health and well-being.
- Seek Prompt Medical Attention: Despite taking preventive measures, foot ulcers may still occur in some diabetics. In such cases, it’s crucial to seek prompt medical attention to prevent complications. Healthcare providers can assess the severity of the ulcer, prescribe appropriate treatments such as antibiotics or wound dressings, and provide guidance on wound care and management.
- Practice Wound Care Techniques: Diabetics with foot ulcers should adhere to proper wound care techniques to facilitate healing and prevent infections. This may include cleaning the wound with saline solution, applying prescribed medications or ointments, and dressing the wound with sterile bandages or dressings. It’s essential to follow healthcare provider instructions closely and seek assistance if any complications arise.
- Monitor for Signs of Infection: Individuals with foot ulcers should monitor for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, warmth, or drainage from the wound. If any of these symptoms occur, it’s vital to seek immediate medical attention, as untreated infections can lead to serious complications, including systemic infections or sepsis.
- By incorporating these additional tips into their foot care routine, individuals with diabetes can further reduce their risk of developing foot ulcers and enhance their overall foot health and quality of life.