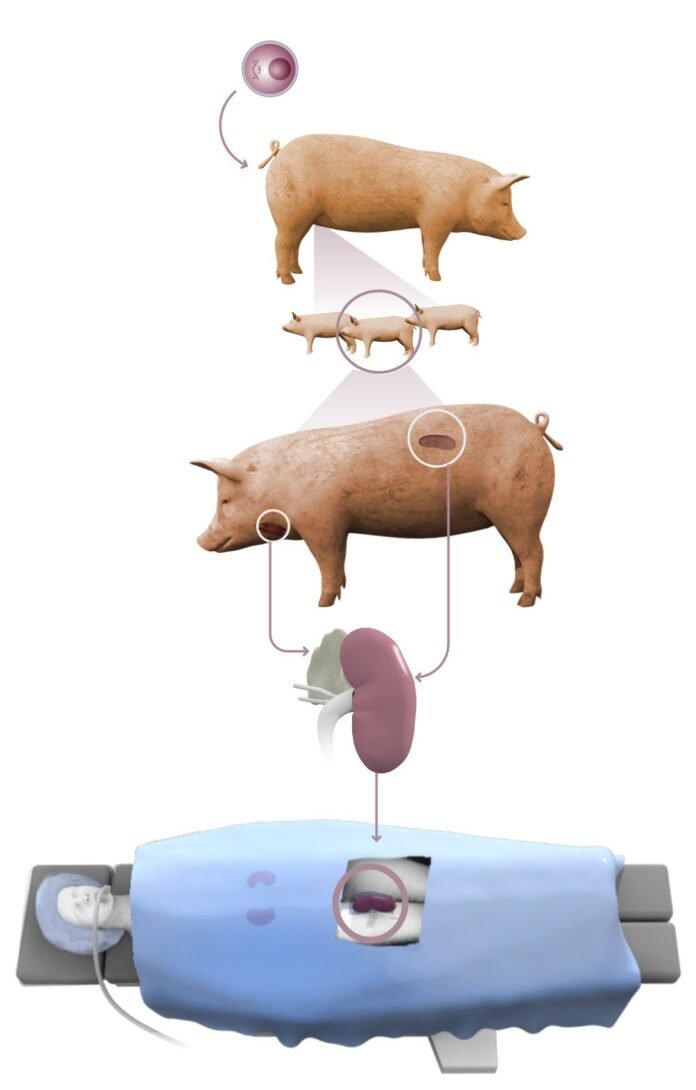
Pig kidney transplantation, or xenotransplantation, has emerged as a potential solution to address the critical shortage of human organs available for transplantation. With the demand for organs far surpassing the available supply, medical researchers have turned to alternative sources, such as pigs, due to the anatomical similarities between their organs and those of humans.
Dr. Puneet Bhuwania, a consultant nephrologist and transplant physician at Wockhardt Hospitals, Mira Road, emphasized the advantages of using pig kidneys in transplants. He highlighted that pigs have anatomical features similar to human organs, making them suitable candidates for xenotransplantation. Additionally, pigs have shorter lifespans compared to humans, allowing for a more immediate availability of organs for transplantation.
Despite the potential benefits of pig kidney transplants, there are several factors to consider regarding the sustainability and long-term viability of this approach. One key concern is the risk of organ rejection by the recipient’s immune system. As xenotransplantation involves introducing foreign tissue into the human body, there is a heightened risk of immune rejection, which could compromise the success of the transplant.
To address this challenge, researchers have been exploring various strategies to minimize the risk of rejection and improve the compatibility between pig organs and human recipients. This includes genetic modification of pigs to produce organs with reduced immunogenicity, as well as advancements in immunosuppressive therapies to prevent rejection post-transplantation.
Additionally, ethical considerations surrounding xenotransplantation remain a topic of debate within the medical community and society at large. Questions regarding animal welfare, potential transmission of infectious diseases from pigs to humans, and the implications of genetically modifying animals for organ transplantation raise complex ethical dilemmas that must be carefully considered.
While pig kidney transplants offer a promising avenue to alleviate the organ shortage crisis and save lives, further research and clinical trials are needed to address the existing challenges and ensure the safety and efficacy of this innovative approach. Ultimately, the future of xenotransplantation will depend on advancements in medical science, ethical deliberations, and regulatory frameworks aimed at balancing medical progress with ethical considerations and patient safety.
As researchers continue to explore the potential of pig kidney transplantation, ongoing studies are focusing on refining the techniques and protocols involved in xenotransplantation. One area of interest is the development of immunomodulatory strategies to induce tolerance and prevent rejection of pig organs by the recipient’s immune system.
One approach involves the use of specialized cells, such as regulatory T cells, to suppress immune responses and promote tolerance to the transplanted organ. By harnessing the body’s own regulatory mechanisms, researchers aim to create an environment conducive to long-term acceptance of pig kidneys in human recipients.
Furthermore, advancements in genetic engineering techniques have enabled scientists to modify pigs at the genetic level to produce organs with enhanced compatibility and reduced immunogenicity. By introducing specific genetic modifications, such as the deletion of genes associated with hyperacute rejection, researchers can create pigs whose organs are less likely to be rejected by the recipient’s immune system.
In addition to addressing immunological barriers, researchers are also investigating strategies to mitigate the risk of infectious disease transmission associated with xenotransplantation. Rigorous screening protocols and monitoring procedures are implemented to ensure the safety of both the donor pigs and the transplant recipients. Additionally, ongoing surveillance efforts aim to identify and address any potential risks of zoonotic disease transmission.
Ethical considerations surrounding xenotransplantation extend beyond the welfare of animals and encompass broader societal implications. Questions regarding equity in access to transplantation, the allocation of organs, and the commodification of animals for medical purposes are central to ethical debates surrounding xenotransplantation.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of pig kidney transplantation cannot be overlooked. For patients facing end-stage organ failure, xenotransplantation offers a glimmer of hope and the possibility of extending and improving their quality of life. By expanding the pool of available organs and reducing reliance on human donors, pig kidney transplantation has the potential to transform the field of organ transplantation and save countless lives.