In a groundbreaking move, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has given its approval for a cutting-edge gene-editing treatment for sickle cell disease. The newly approved therapies, Casgevy and Lyfgenia, stand as pioneering cell-based gene treatments, with Casgevy leveraging the power of the Nobel Prize-winning CRISPR gene-editing tool.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Severity of Sickle Cell Disease
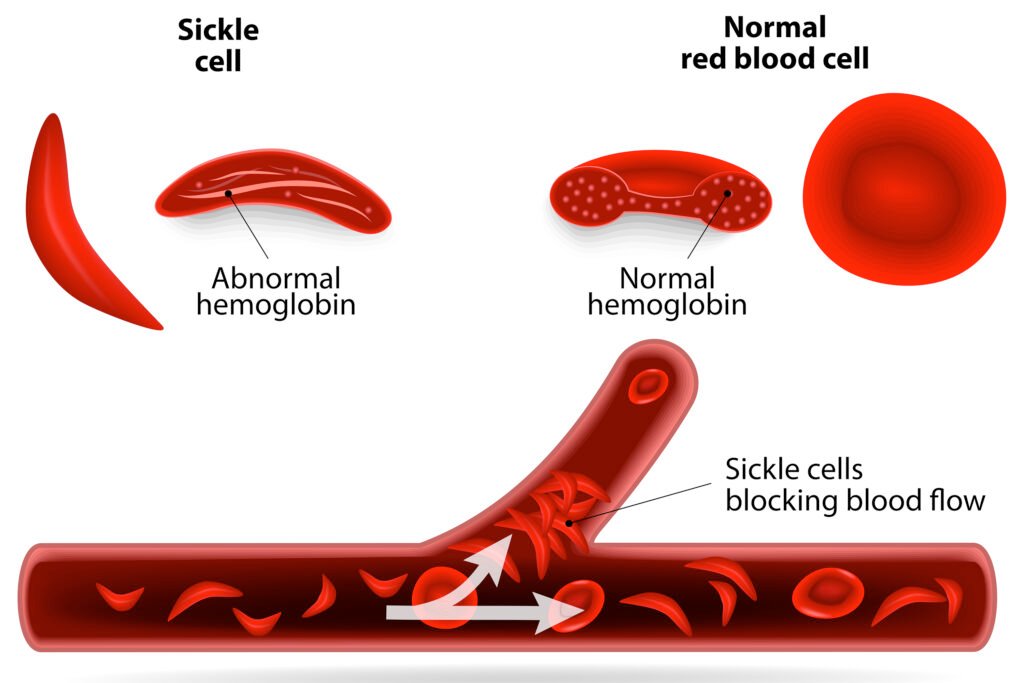
Sickle cell disease is an uncommon yet debilitating blood disorder with life-threatening implications. FDA’s Dr. Nicole Verdun emphasized the significance of these approvals, particularly for individuals whose lives are profoundly impacted by this disease. Globally, over 7.7 million people, primarily of African or Caribbean descent, grapple with the challenges posed by this condition. The disease triggers the formation of elongated blood cells, leading to blockages in blood vessels, compromised oxygen supply, and severe complications like excruciating pain, strokes, and organ damage.
Casgevy’s Gene Editing Mechanism
Casgevy, or Exa-cel, zeroes in on the problematic gene within a patient’s bone marrow stem cells. This intervention prompts the production of properly functioning hemoglobin—the essential oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells. The treatment involves administering chemotherapy, extracting stem cells, conducting lab-based treatment using the CRISPR gene-editing tool to eliminate the DNA segments causing the sickle shape, and reintroducing the treated stem cells into the patient’s body.
Lyfgenia: An Alternative Gene Therapy
In addition to Casgevy, the FDA has given the green light to Lyfgenia, introducing another gene therapy for sickle cell disease. Lyfgenia takes a different approach, utilizing a harmless virus to insert a gene into patients’ stem cells, offering an alternative avenue for addressing the condition.
Overcoming Previous Treatment Challenges
Before the advent of these groundbreaking treatments, individuals with sickle cell disease had limited options, including medications and blood transfusions. The sole permanent solution was a bone marrow transplant, necessitating a closely matched donor without the disease, while carrying the inherent risk of rejection.
Future Considerations
The FDA’s approval of Casgevy and Lyfgenia marks a significant leap forward in the treatment landscape for sickle cell disease. Despite these groundbreaking strides, concerns loom regarding the potential high costs associated with gene therapy treatments, potentially limiting accessibility for those in dire need. As these therapies usher in a new era of treatment possibilities, ensuring widespread availability and affordability will be paramount for their positive impact on the lives of individuals grappling with sickle cell disease.